Complex Phase Steel: An Introduction
WHAT IS COMPLEX PHASE STEEL?
Complex Phase steel (CP steels) is a part of the Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) family.
Complex Phase steels gain their strength through extremely fine grain size and micro structure containing small amounts of martensite, pearlite and retained austenite embedded in a ferrite-bainite matrix. High grain refinement is achieved by precipitation of micro alloying elements such as Nb, Ti or V or retarded recrystallization.
Complex Phase steel is being produced as both hot-rolled and cold-rolled which can be hot dipped galvanized for corrosion protection. Hot-rolled products are available in the higher thickness ranges needed to produce structural type parts.
The chemistry and microstructure of CP steels is similar to Trip Steels, except for the addition of some quantities of the Nb, Ti and or V to cause a precipitation strengthening effect.
The bainite complex phase microstructure exhibits improved strain hardening and strain capacity over the bainite structure alone.
Properties of CP steel
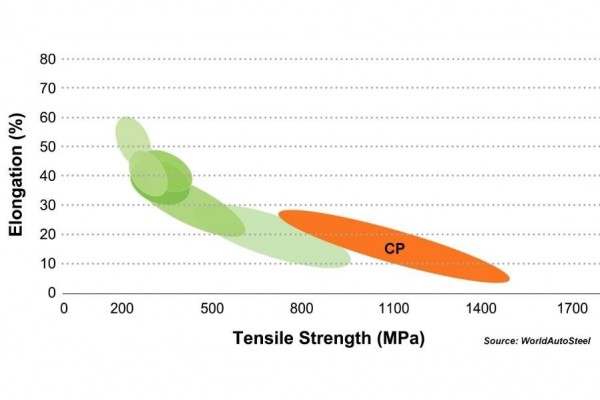
CP steels have a higher minimum yield strength in comparison with dual phase steels of identical tensile strengths of 800 Mpa and greater. When compared to DP steels, CP steels have a much higher yield strength to tensile strength ratio.
CP steels have high work hardening capability at low strain, high fatigue strength, high energy absorption, wear resistance and bake hardening potential.
Heat treatment of hot-rolled CP steels at 500-700 C can further increase the yield point of the material by up to 100 MPa.
CP steels are readily welded to itself or other common grades of steel, spot welders for other lower strength grades can be used with the appropriate adjustments.
Current and developmental strength grades range from 780 to 1470 Mpa minimum tensile strength with 5-30% total elongation.
Formability
With high uniform elongation and continuous yielding CP steels have excellent formability and are suitable for stretch forming, roll-forming, bending and hole expansions.
Applications of CP steel
Due to CP steels high capability to absorb energy during a collision they are particularly well suited for weight saving manufacturing of cold formed crash relevant parts in automobiles. There are several automotive applications in body structure, suspension and chassis components.
Current production grades of CP steels and examples of automotive applications:
- CP 600/900 Frame rails, B pillar reinforcements, tunnel stiffener
- CP 680/780 Frame rails, chassis components, cross members
- CP 800/1000 Suspension brackets, fender beams
- CP 1000/1200 Frame rail reinforcements, rocker panel supports
- CP 1050/1470 Bumper beams, side sills
To summarize complex phase steels’ properties:
- Tensile strengths that meet and exceed 800 MPa
- High ratio of yield to tensile strength
- Great for cold forming, bending, and hole expansion
- Strong bake-hardening qualities
- High durability and wear resistance
- High crash energy absorption
- Good weldability
About National Material L.P. – With more than 3,000 employees from a multinational portfolio of companies, NMLP provides engineered metal products, which include steel processing, aluminum extrusion and stainless steel rolled product companies, to automotive, aerospace, construction, defense, electrical, and industrial markets.
Visit National Material: https://www.nationalmaterial.com or call (U.S.) 847-806-7200, Diana Pulido